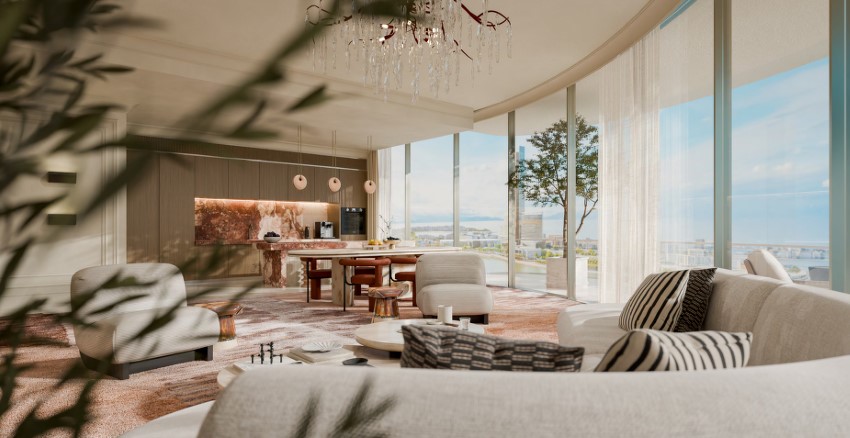
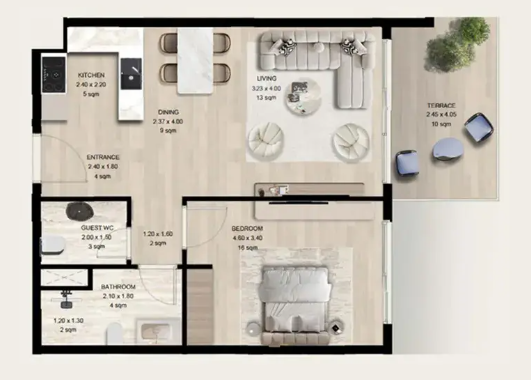
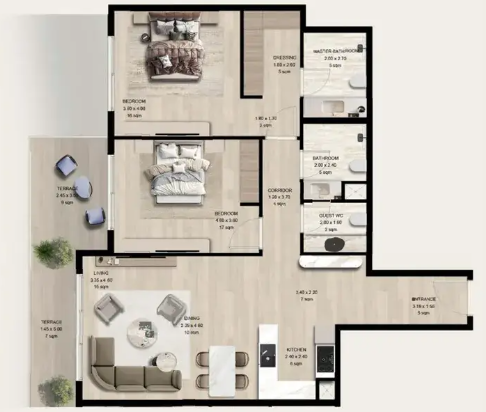
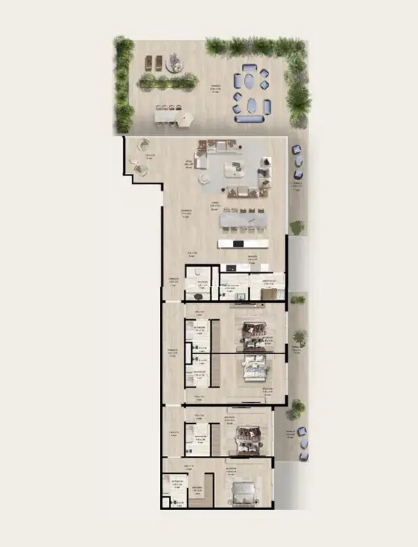
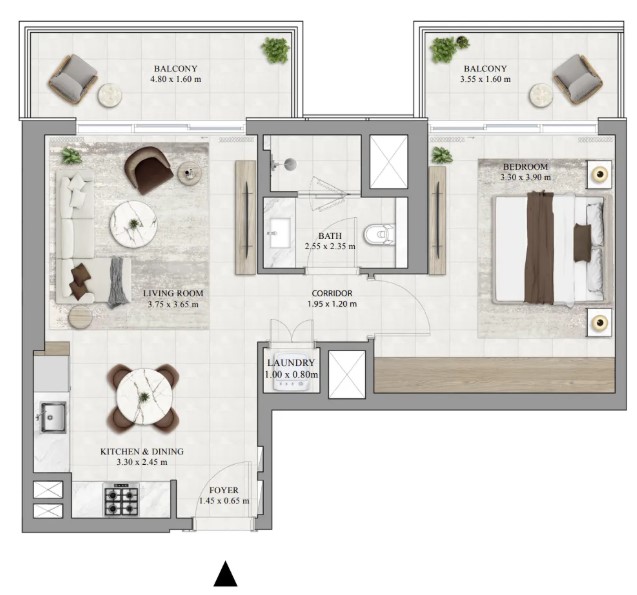
Find the right property in Dubai & UAE for your investment goal
Invest with clarity.
Buy with confidence.
DATA LEAD
MARKET EXPERTISE
CARE & SUPPORT
We guarantee the best price on the market.
No bias. Find the property that much first your interest not the broker’s



Why VALORISIMO ?
We’re not a brokerage. We’re not a listings site. We’re something new.
A trusted investment partner that puts the buyer first – always.
Insight,
Not Hype.
Every recommendation is backed by market data and aligned with your goals.
Expert Support,
End-to-End.
We guide you from property search to purchase – and beyond.
Buyer-First
Philosophy.
No sales pressure. No hidden agendas. Just honest, practical advice.
How it works
Here’s how we simplify the process.

01. Tell us about your goals
– via our Smart Matching Tool
02. Get tailored property matches
– backed by real-time market data
03. Speak to an expert
– for personalized advice
04. Buy with confidence
– with ongoing support, even after purchase

The Valorisimo View
Key trends from the Dubai and Abu Dhabi property markets – with insights from our team to help you invest smarter.
Meet the People
Behind Valorisimo
Real people, real expertise – and a genuine passion for helping you invest smarter.
Curated
by Experts
We only feature properties that meet our standards – based on value, yield, and long-term potential.
UAE Investment Guides
Everything you need to know about investing in the UAE – from market insights to practical tips, explained simply.
Location Matters.
We Break It Down.
Understand the market, lifestyle,
and investment potential of every
major district.

Dubai Marina – Waterfront Living, High Rental Yield | VALORISIMO
Welcome To Dubai Marina Dubai Marina is one of Dubai’s most vibrant waterfront communities, known for its stunning skyline, luxurious residences, and lively atmosphere. This

Business Bay – Executive Living & Prime Real Estate in Dubai
Welcome to Business Bay in Dubai Business Bay is one of Dubai’s most strategic mixed-use districts, offering a seamless blend of upscale residences, world-class commercial

Palm Jumeirah – Iconic Island Living & Elite Real Estate Investment
Welcome to Palm Jumeirah in Dubai Palm Jumeirah is Dubai’s most iconic man-made island and a globally recognized symbol of luxury and innovation. Designed in
The Valorisimo Journal
Dive into expert takes on the UAE property market, investment tips, and smart buying strategies.
Find the Right Property for You.
Whether you’re a first-time investor or growing your portfolio, we’ll help you buy with confidence.
What Our
Clients Say
Real stories from buyers who’ve trusted Valorisimo to guide their investments.
Data-Driven Confidence
alorisimo completely changed how I approached real estate investing. Their data-driven insights helped me identify a high-growth neighborhood I hadn’t considered before. I closed on my property with full confidence, knowing it aligned perfectly with my financial goals.
A Personalized Experience
As a first-time investor living abroad, I felt overwhelmed by the complexity of the market. Valorisimo simplified everything with its tailored recommendations. The platform matched me with a project that fit my budget and objectives within minutes! !
Effortless Decision-Making
Finding the right investment project used to take weeks of research. With Valorisimo, I found a top-rated project in just one evening. Their transparent analysis and neighborhood comparison tools saved me time and gave me peace of mind.